Tuning server performances
As many PHP frameworks, Pydio ends up loading quite a lot of PHP files at runtime, which can result in poor performances if the server is not correctly configured. Furthermore, managing files, and particularly big files, can also lead PHP to high CPU load for some operations. We present here the basic strategies that can be implemented to enhance performance, from easy (and really recommanded) to more complex setups.
Install a PHP Accelerator
It is REALLY RECOMMENDED to use a PHP Accelerator when running Pydio. As any PHP framework, we load and read a lot of PHP files at runtime (all classes), and using an accelerator will simply “precompile” the files (turn them into opcode) and cache the code in memory, avoiding the retriggering this operation at each request. This will generally really improve the performance, dividing by two or three each request time.
PHP APC is a recommended choice, but other accelerators may do the job as well.
Execute actions asynchronously
Although not as good as NodeJS to provide such behaviour, PHP offers a way to send display results to the users before actually performing some actions. The Event system of Pydio takes party of this to improve the user experience and perceived performance. To make sure this is working, please check that php output_buffering is DISABLED for your virtual host.
To go further, many events like sending notifications on files operation can be performed really asynchronously, by storing them inside a queue and triggering the queue processing via a CRON job. To do that, you must enable the feature in Global Configurations > Core Configs > Message Queuing, making sure to have defined an mq instance (SQL is recommended here).
Then you will have to set up a CRON job using the CLi version of the framework, that will trigger the queue processing. Add the following line to your crontab, for example on a 5minutes cycle :
php /path/to/pydio/cmd.php -u=admin -p=password -r=ajxp_conf -a=consume_notification_queue
Delegate download operation to Apache
In PHP, reading a file to the output buffer for downloading can prove a CPU-consuming task. If you encounter CPU peaks during downloads, you should consider using the XSendFile extension. Originally an NGinx extension, there is also an apache port (mod_xsendfile), and the idea is that once the Pydio framework has done the necessary checks to let a user download a file, it will actually send a header to Apache and return, letting Apache server the file, which it does quite well.
You first have to correctly install & configure XSendFile, making sure that the authorized pathes include the real path to the workspace roots on the server. Then activate XSendFile support inside the access.fs plugin global options.
Delegate Zip operation to server
Same as download, the ZIP operation necessary for multiple download of files can end up a very long operation if your users want to download a whole, deep folder at once. To avoid hogging the system, use the access.powerfs plugin to actually delegate this compression to the underlying server.
This requires having the ZIP utilitary available through the command line (working ok on Linux & Windows systems), and when triggering a full folder download, Pydio will launch a zip command on the OS, monitor its progress and display the percentage to the user, and once it’s done, trigger a download of the created archive.
You can enable this feature by going to All Plugins > Available Plugins > Action Plugins and enable Zip Delegation.
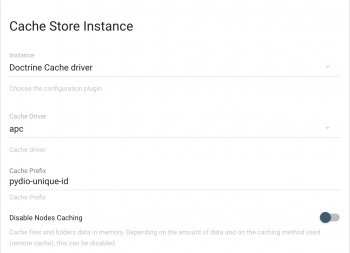
Make use of a Cache Server mechanism
Caching helps in consistently reducing hefty/slow operations and minimizing system resources needed to load a page. Thus boosting the performance to a great extent. Pydio provides an option to configure third party vendor's caching service with pydio.
Though caching service was introduced in pydio v6.2.X, the ease of configuring it has been greatly enhanced in the later versions. Now you can directly configure the caching options from Pydio admin panel.
Along with the PHP Accelerator (PHP APC) pydio provides memcache, memcached, redis, xcache options by default to configure cache server.. The NOSQL keyvalue stores like memcache, memcached and Redis runs a server on a local port to provide the caching service.
Back to top